Most Popular Articles this Week
August 30, 2023
Is 5G security being sacrificed at the altar of profit, politics and process?
Homo sapiens is an incredibly adaptable species, arguably the most adaptable ever. But it is also a forgetful one, quick…
November 22, 2019
Collaboration: The Unexpected Key to Success in Canada’s 5G
In 1967, Lynn Margulis, a young biologist, published a paper that challenged more than a hundred years of evolutionary theory.…
October 4, 2020
5G in Manufacturing – 5G and Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) for Industrial Automation
In the recent report by IHS Markit – “The 5G Economy – How 5G will contribute to the global economy”…
March 21, 2020
Unlocking the Future – Why Virtualization Is the Key to 5G
Depending on who you speak to, 5G is either humankind’s greatest imminent blessing or its greatest imminent curse. Still in…
August 26, 2019
AI and 5G: AI at the 5G Core – A Double-Edged Sword
If you’ve ever been to an expensive restaurant and ordered a familiar dish like, say, lasagna, but received a plate…
November 4, 2019
The Quantum Computing Threat
Recently, in the science journal Nature, Google claimed ‘quantum supremacy’ saying that its quantum computer is the first to perform…
April 1, 2019
Geopolitics of 5G and 5G-Connected Massive & Critical IoT
Emerging Technology and Geopolitics of 5G There are several reasons emerging technology is a highly competitive industry, notwithstanding the race…
May 17, 2021
Securing Society 5.0 – Overcoming the hidden threats in society’s greatest evolutionary leap
A term first coined by the Japanese government, “Society 5.0” describes “A human-centered society that balances economic advancement with the…
April 9, 2019
5G Critical Infrastructure – the Most Critical of All
Not even 30 years separate us from the end of the Cold War. Yet, we appear to be witnessing the…
January 1, 2024
Marin’s Statement on AI Risk
The rapid development of AI brings both extraordinary potential and unprecedented risks. AI systems are increasingly demonstrating emergent behaviors, and…
March 16, 2019
How 5G Will Transform Economy and Society
Since the dawn of the 21st Century, the ways in which people and organizations that use the Internet experience, perceive…
March 26, 2019
5G Policy and Regulatory Checklist
Ultra high speed, high quality 5G networks are expected to provide the connectivity required for massive IoT adoption, remote robotic…
February 28, 2021
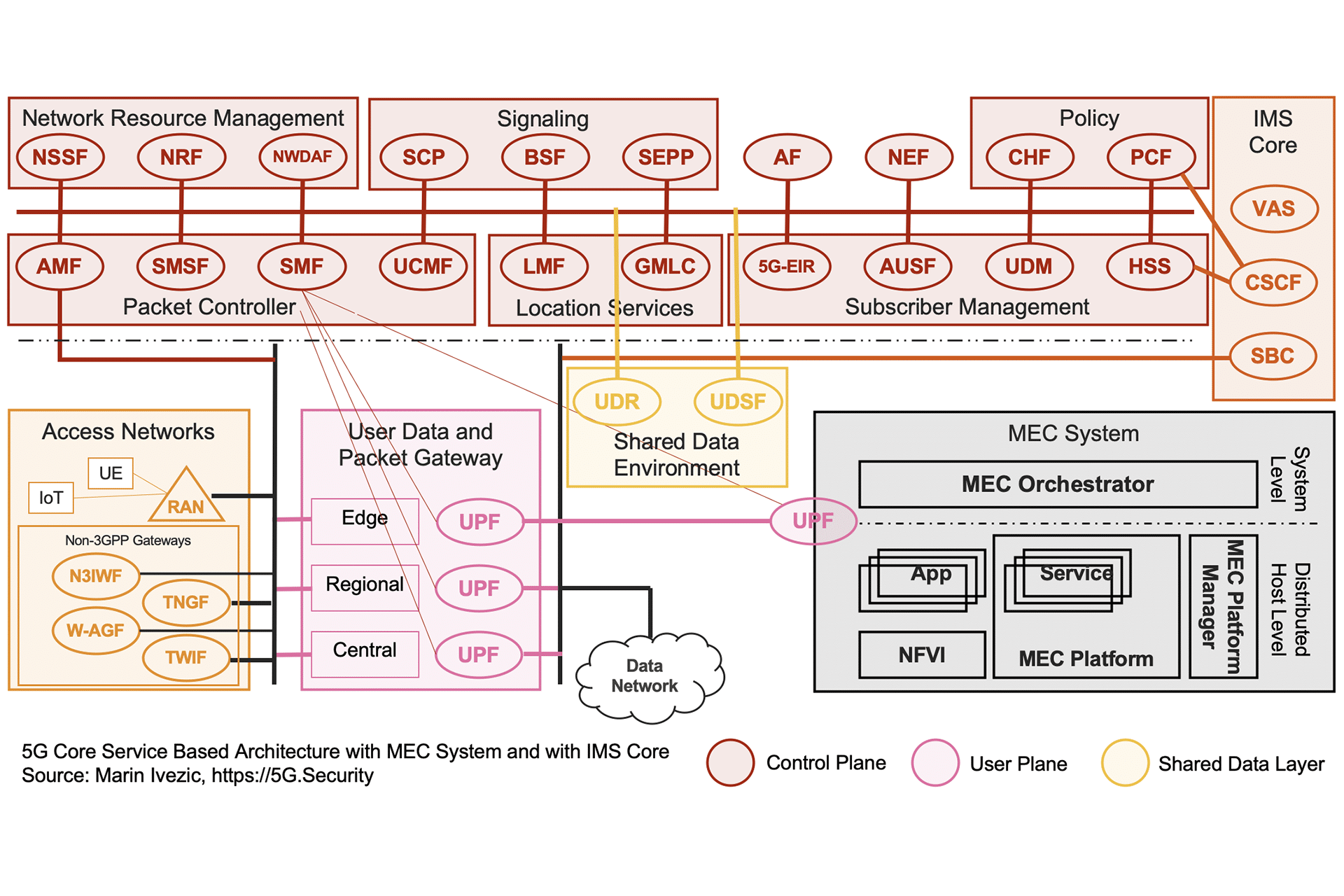
A Comparison of 5G Core Network Architectures
The 5G Core network is a Service Based Architecture. It evolves the traditional appliance based 4G Core Network to support…
February 17, 2020
Will 5G and Society 5.0 Mark a New Era in Human Evolution?
In their outstanding book, Wicked and Wise, Alan Watkins and Ken Wilber look at some of the most pressing ‘wicked…
March 25, 2019
5G Network Slicing Technology: A Primer
Hyped as the technology that will transform the world, 5G is moving past the buzzword stage with first implementations coming…
May 3, 2019
Digital Double Helix: Why the Fates of 5G and AI are Intertwined
In 2013, George F. Young and colleagues completed a fascinating study into the science behind starling murmurations. These breathtaking displays…
August 16, 2020
Introduction to 5G Core Service-Based Architecture (SBA) Components
The interest in 5G and mIoT is exploding. It’s exciting to see so many IT and cybersecurity professionals in my…
November 27, 2020
Open RAN May Be the Future of 5G, but Can We Keep It Secure?
It’s been a year of contradictions for the telecommunications industry. Like most sectors, it has been heavily impacted by the…