Share via:
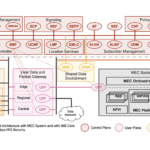
National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) of the United States Department of Commerce published “Open RAN Security Report” outlining cybersecurity considerations associated with using Open Radio Access Networks (Open RAN) as an approach to developing network architecture. The report provides an in-depth analysis of the security implications associated with Open Radio Access Networks (Open RAN), comparing them to traditional RAN deployments. The report concludes that Open RAN does not significantly alter the overall security risk landscape in telecommunications. It finds that the majority of security threats are common to both Open RAN and traditional networks, with only a minimal percentage unique to Open RAN. However, effective mitigation strategies can ensure comparable security levels in both deployment types.
Key observations from the report include:
- A slight increase in the network’s vulnerability (“attack surface”) with Open RAN compared to traditional RAN.
- Similar risks related to cloud-based infrastructure usage in both Open RAN and traditional networks, as well as for other cloud-reliant technologies.
- Issues concerning artificial intelligence, machine learning, and open-source software are not exclusive to Open RAN and can be managed.
Open RAN brings several security advantages, such as the ability for operators to independently test and verify security controls, more efficient addressing of security issues in cloud-enabled environments, and improved operational visibility through automation. The report also highlights non-security benefits like enhanced vendor competition, reduced vendor lock-in, potential cost and performance improvements, and optimized energy efficiency.
Nevertheless, Open RAN introduces new security considerations. The increased number of vendors in the supply chain could complicate coordination and necessitates that operators take responsibility for the reliability and trustworthiness of their supply chains. It is essential for Open RAN vendors, systems integrators, and operators to rigorously analyze and strengthen their technologies against vulnerabilities. The diversification in suppliers and technology components in RAN deployments may also challenge the management of all software used.
The report concludes by outlining various mitigation strategies for operators currently deploying or considering Open RAN. It emphasizes that the technical specification of Open RAN security requirements is an ongoing process. Operators should implement supplementary controls throughout the Open RAN lifecycle and adhere to widely recognized industry standards and best practices, including thorough security evaluations of equipment.
The full report is available here: https://www.ntia.gov/report/2023/open-ran-security-report
Marin Ivezic
For over 30 years, Marin Ivezic has been protecting critical infrastructure and financial services against cyber, financial crime and regulatory risks posed by complex and emerging technologies.
He held multiple interim CISO and technology leadership roles in Global 2000 companies.
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkNovember 17, 2022
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkSeptember 20, 2022
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkApril 27, 2022
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkMarch 25, 2022
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkFebruary 8, 2022
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkFebruary 4, 2022
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkFebruary 28, 2021
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkFebruary 24, 2021
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkFebruary 21, 2021
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkJanuary 20, 2021
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkNovember 27, 2020
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkSeptember 27, 2020
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-linkMay 16, 2020
-
Marin Ivezic#molongui-disabled-link